Next: Wheel mesh Up: Mesh Generation using snappyHexMesh Previous: Background mesh Contents Index
Mesh motion
The unsteady (transient) case can be run from the initial values of fields given in the settings for zero time (next section) or from results of a steady-state computation. The usage of converged steady-state simulation to initialize the transient case can be generally advised, because it will noticeably speed up the convergence of the unsteady (transient) simulation. For this reason we give here listings of settings for both MRF method (steady-state) and SBM method (transient).
The steady-state method MRF (multiple reference frame) uses the file system/fvOptions:
MRF1
{
type MRFSource;
active true;
selectionMode cellZone;
cellZone rotorMRFZone;
MRFSourceCoeffs
{
nonRotatingPatches
(
wheel_inlet_2_ami
wheel_outlet_1_ami
);
origin (0 0 0);
axis (0 0 1);
omega 209;
}
}
bound_T
{
type temperatureLimitsConstraint;
selectionMode all;
active true;
temperatureLimitsConstraintCoeffs
{
Tmin 250;
Tmax 400;
}
}
It contains two sections, of which only the first one is concerned with rotation. The second one (bound_T) is just a constraint for temperature that will inhibit wild changes in temperature in the beginning of the simulation. In the present setting it will bound temperature to the interval 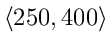 K. The first section (MRF1) will create a new MRF zone – the rotating part of the mesh – from the cell zone “rotorMRFZone”. We have created the cell zone for wheel using topoSet in the section
K. The first section (MRF1) will create a new MRF zone – the rotating part of the mesh – from the cell zone “rotorMRFZone”. We have created the cell zone for wheel using topoSet in the section ![]() .
.
The unsteady (transient) method SBM (solid body motion) uses the file constant/dynamicMeshDict:
dynamicFvMesh solidBodyMotionFvMesh;
solidBodyMotionFvMeshCoeffs
{
solidBodyMotionFunction rotatingMotion;
cellZone rotorMRFZone;
rotatingMotionCoeffs
{
origin (0 0 0);
axis (0 0 1);
omega 209;
}
}
The keywords origin and axis specify the axis of rotation, the keyword omega the angular frequency of rotation. There are more motion functions in OpenFOAM; here we use rotatingMotion that will rotate the cells of rotorMRFZone. For other motion functions list the appropriate directory of the source:
# cd $FOAM_SRC/dynamicFvMesh
# ls solidBodyMotionFvMesh/solidBodyMotionFunctions
Solid body motion engine transforms the mesh on every iteration by moving points selected by the cell zone. It also recalculates the fluxes, so that the flow fields are compatible with the new wall positions etc.
Next: Wheel mesh Up: Mesh Generation using snappyHexMesh Previous: Background mesh Contents Index