Previous: Test case description Up: Test case: External Aerodynamics Next: The Flow around the
This is an automatically generated documentation by LaTeX2HTML utility. In case of any issue, please, contact us at info@cfdsupport.com.
Parabolic velocity profile in boundary layer
- Assuming parabolic profile in boundary layer one should create an inlet boundary condition according to those assumptions.
- One can use standard boundary condition of the type fixedValue and our custom utility setVelocityProfile computes the nonuniform velocity distribution at the inlet.
- The equation of velocity parabolic profile in boundary layer is derived from Navier-Stokes equations,
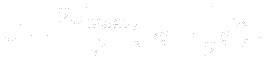
Here ![]() is the boundary layer thickness and
is the boundary layer thickness and ![]() is the velocity of the main stream.
is the velocity of the main stream.
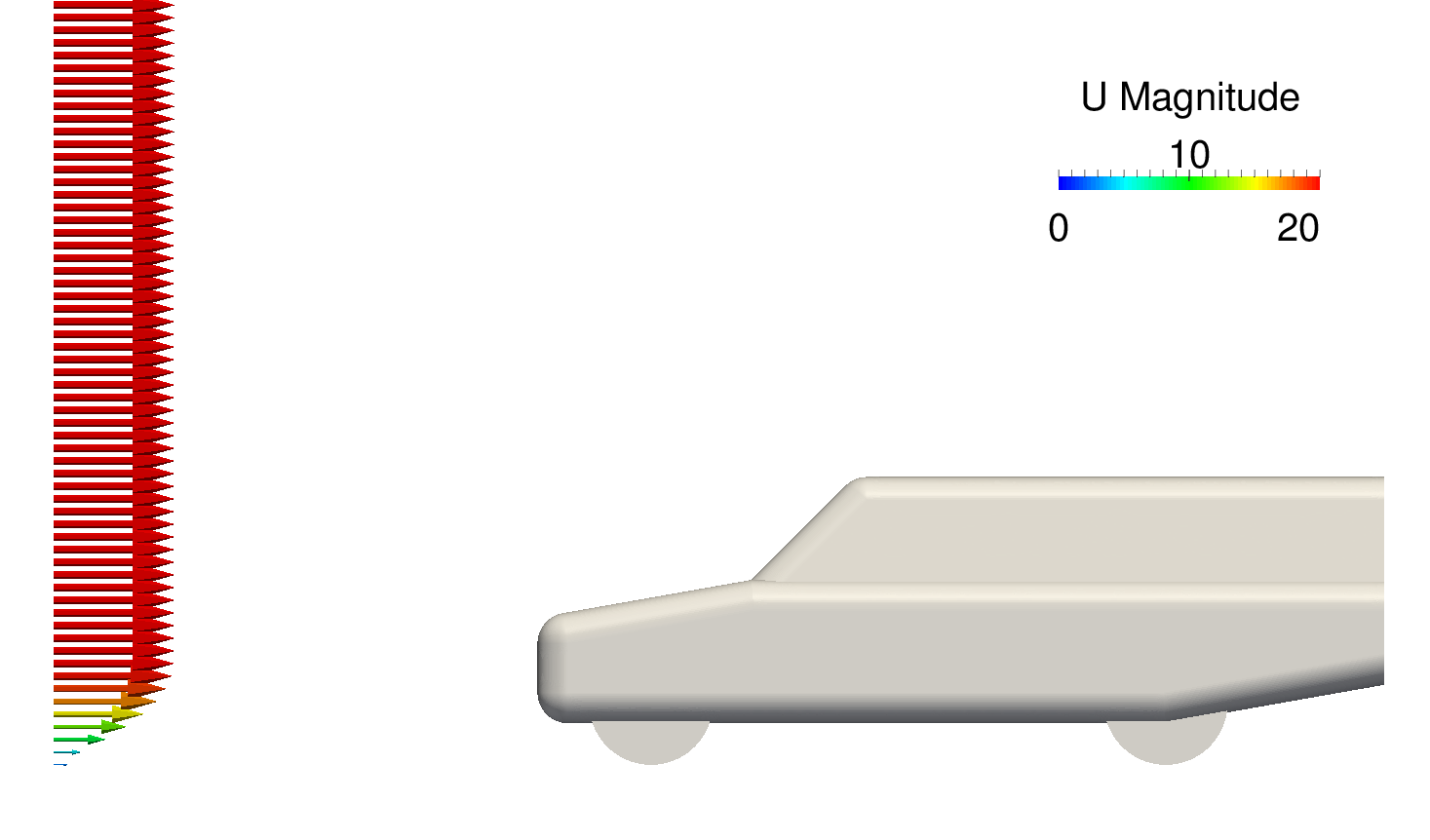
Figure: Parabolic profile
- Utility setVelocityProfile sets the parabolic velocity profile at the inlet patch
- The velocity profile represents the boundary layer with respect to the equation
![Node258 11 [*]](http://www.cfdsupport.com/img/crossref.png)
double Umain = Upatch[patchi].x(); forAll(faceCentres, facei) { double fcY = faceCentres[facei].y(); if(fcY <= L) Upatch[facei].x() = (2.0*Umain/(L*L))*(L*fcY-0.5*fcY*fcY); else Upatch[facei].x() = Umain; } - The source code of the utility is present in the training materials in folder setVelocity.
- Copy utility folder and compile it using wmake:
# mkdir -p $WM_PROJECT_USER_DIR/applications/utilities
# cp -r .../training/applications/utilities/setVelocity \
$WM_PROJECT_USER_DIR/applications/utilities/
# cd $WM_PROJECT_USER_DIR/applications/utilities/setVelocity
# wmake - After a successful compilation the utility can be run from the root directory of any test case using the command setVelocityProfile.